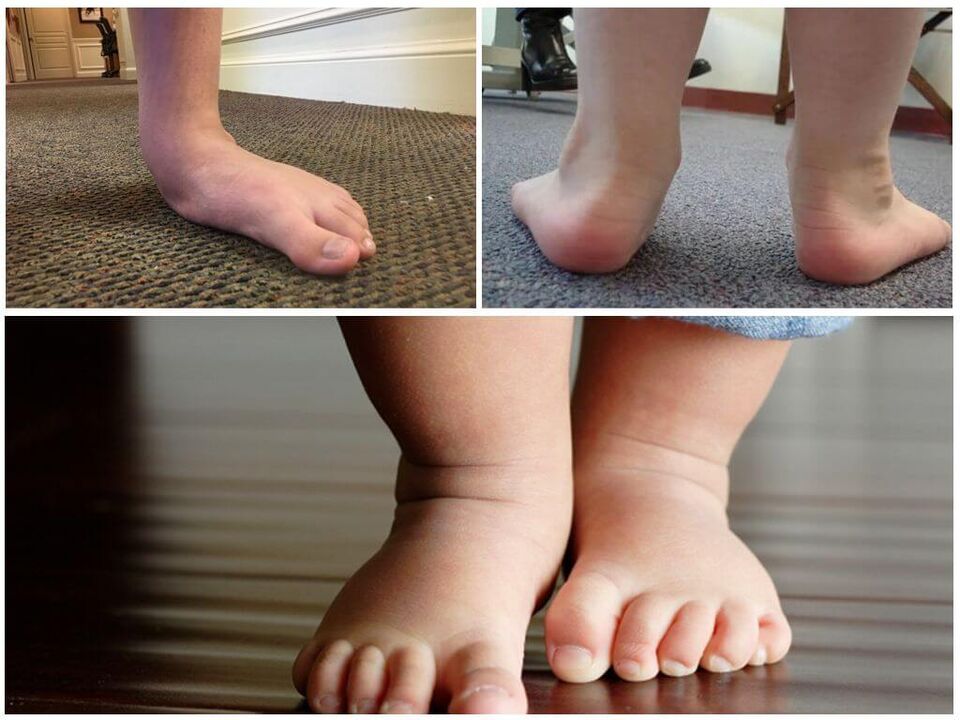
Hallux valgus is a disease more common among children and women and is orthopedic in nature. It is distinguished by the curvature of the axis of the foot, when its central part descends and thickens. Additionally, a deformity of the big toe, a characteristic protuberance and muscle-ligament balance may appear.
Other names for the disease: hallux valgus, hallux valgus.
Main symptoms: pain, fatigue when walking, curvature of the axis of the foot.
Treatment is carried out by an orthopedist-traumatologist.
An article for patients with a disease diagnosed by the doctor. It does not replace a visit to the doctor and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
Causes
Valgus deformity of the feet almost always has a complex nature of formation. In most cases, there are combinations of the following prerequisites:
- Flat feet, both congenital and acquired. Due to its presence, weight and pressure are distributed unevenly, which leads to deformation of the fingers.
- Osteoporosis, characterized by loss of bone rigidity and low calcium content.
- Obesity, excess weight, which causes excessive stress on the bones, especially with muscle weakness.
- Hereditary predisposition, when the ligaments are weak, as well as characteristic changes in the foot - hallux valgus - can be genetically predetermined.
- Wearing the wrong shoes. The problem often occurs in women because they walk in uncomfortable, narrow shoes with high heels. In this case, the correct load on the foot is disrupted and the likelihood of hallux valgus deformity increases.
- Injuries, for example, a heavy object falling on the leg, a fracture or bruises can cause the foot to deform.
- Concomitant diseases of the endocrine system, neurological nature.
- Strong fluctuations in hormones, including during menopause, during pregnancy and during the natural course of the menstrual cycle.
Bunions can occur for any of these reasons, as well as a combination of them. However, it is not always possible to objectively determine the exact basis for the development of hallux valgus. In this case, the greatest emphasis is placed on the course of therapy.
Phases and forms
One of the main criteria for assessing the severity of foot deformity in children and adults is the angle of deviation of the big toe. The larger it is, the more severe the degree of pathology. According to her:
- Stage I -15°;
- II - 20°;
- III - 30°;
- IV - more than 30°.
Fully evaluate the degree of hallux valgus deformation not only of the first toe, but also of the rear one. There is a classification based on the installation of the heel relative to the axis of the shin:
- Stage I - presence of flat feet, but a slight deviation up to 15°;
- II - up to 23°;
- III - up to 30°;
- IV - the foot becomes completely flat, the deviation is more than 30°, which is considered a severe form.
In general, depending on the severity of the situation and the degree of curvature, the following types of disease course are distinguished:
- lung;
- average;
- heavy.
Due to the formation, foot deformities are divided into the following types:
- structural, which is caused by congenital pathology;
- static, caused by the curvature of the spine;
- spastic, resulting from excessive strain or muscle tone;
- traumatic foot deformity;
- stunted and others.
Therefore, there are many types of deformities of the first toe and other parts of the foot. To determine the characteristics of the course of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo tests.
Symptoms
The special insidiousness of the pathology lies in the fact that it does not manifest itself for a long time. Often a person simply does not notice the warning signs, including the formation of calluses in the same places, a quick feeling of tiredness after walking. Noticeable problems begin only when the disease reaches a more severe stage, which complicates treatment and lengthens it.
Manifestations of hallux valgus can vary and include the following:
- fatigue while walking;
- seeds;
- calluses that appear regularly, constantly in the same places;
- Pain;
- increased swelling of the lower extremities;
- deviation of the thumb laterally;
- the formation of a characteristic protuberance, often called a "foot bone";
- deformation of the remaining fingers, which become hammer-like.
As the foot deformity progresses, the patient notices that the shoes he previously wore no longer fit. He becomes tight and uncomfortable due to the increasing thickening of the tissues, the appearance of new calluses and the addition of bunions.
Finding shoes becomes difficult, sometimes almost impossible. In the advanced stages of hallux valgus, the pain constantly intensifies, increases, discomfort in the knee and hip joints is noted, and the load on the spine increases. In the first stage of hallux valgus and other parts of the foot, the patient is usually only concerned with a cosmetic problem.
Complications
One of the terrible consequences of the lack of therapy is not only the progression of the pathology, but also the addition of other problems related to it. Negative consequences can occur with the development of hallux valgus. The most common are the following:
- Bursitis, i. e. inflammation of the synovial bags. This problem manifests itself with swelling and pain in some areas of the foot due to the deformity of the foot joints.
- Osteoarthritis is the destruction of cartilage, leading to reduced joint mobility, pain and gait disturbances.
- Increased load, due to which the knee joint wears out, pressure on the spine increases and arthrosis occurs.
- Formation of a heel spur. In this case, a sharp, almost unbearable pain appears when walking.
- Akilobursitis and other diseases.
Furthermore, hallux valgus always represents a serious aesthetic problem, which is especially noticeable when wearing open shoes. This causes a person great psychological discomfort, which can negatively affect his general psycho-emotional state.
To avoid negative consequences, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment. The medical center employs experienced doctors who help patients with any form and degree of valgus.
Diagnostics
At the initial appointment, the orthopedist-traumatologist carries out a comprehensive examination and examination of the patient. To do this, she visually evaluates the condition of the feet, their position, deviations and determines the presence of deformation of the forefoot. However, this is not enough to draw a definitive conclusion on the extent and nature of the problem, so further studies are ordered.
Instrumental methods
One of the main ways to evaluate hallux valgus is by x-ray in three projections. It allows not only to identify this problem, but also to identify a number of others, including subluxations, dislocations and arthrosis. It is on the basis of the results of this examination that it is possible to estimate the extent of the deviation of the angles, make calculations and correctly prescribe a course of treatment for hallux valgus.
For a more detailed study of the deformation of the hallux valgus or, if necessary, further studies are prescribed:
- Ultrasound can help identify disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels if problems with local circulation are suspected.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will help to exclude other pathologies similar to hallux valgus and get a more detailed picture of the disease.
- Plantography, which allows you to identify and determine the degree of flat foot.
- Podoscopy is an examination of the sole of the foot in a standing position.
There are no specific laboratory research methods for diagnosing hallux valgus in adults and children. Usually the listed examination methods are sufficient, but if necessary the doctor can prescribe additional ones.
Hallux valgus can resemble other diseases, making the differential diagnosis particularly important. Among the most common are:
- gout;
- osteoarthritis;
- arthritis.
The modern medical clinic has the latest diagnostic equipment. This allows you to quickly identify hallux valgus and conduct a comprehensive examination and therapy.
Treatment of hallux valgus
Today, specialists have numerous methods to help patients with foot deformities. Even the first phase of therapy can vary depending on the characteristics of the particular case. If the degree of the disease is already severe, hallux valgus in adults sometimes begins immediately with surgery.
Conservative methods
There are many ways and techniques that help to avoid surgical treatment, especially in the initial stages of the development of the pathology. Among the most common are the following:
- Wear orthopedic shoes. It should be rigidly fixed, with a stable, low heel and an extended toe. In addition, special insoles, supports and other devices can be used to remove excess load from the metatarsal bone. It is important to understand that such treatment for hallux valgus is usually long-term and lasts more than six months, sometimes even a year.
- Physical therapy classes. The physical therapy instructor selects a program for a specific patient and also teaches the correct technique for performing the exercises. It is important to consult a specialist in the first stage.
- Foot massage. It should be done only in specialized medical centers, since it is aimed not so much at relaxation, but at the treatment of valgus.
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, both to reduce the inflammatory process and to relieve pain. It is important to consult a doctor before using such drugs.
- Proper nutrition, diet enriched with calcium.
In addition, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment of hallux valgus is useful, which may include:
- phonophoresis;
- UHF;
- magnetotherapy.
During the treatment of hallux valgus it is advisable to avoid standing for long periods and to concentrate your efforts on strengthening the muscles and ligaments.
All of these methods for treating hallux valgus can be used in combination or separately. The course is developed by the doctor depending on the situation and complexity of the particular case. However, they are best suited for treating patients with early-onset or early-stage hallux valgus.
Surgical methods
If conservative treatment of foot deformities is ineffective or if the problem is detected at an advanced stage, surgery is performed. It has its advantages, since the problem is solved in one stage, while with non-surgical treatment of deformities of various parts of the foot, it often takes several years.
Today doctors perform the appropriate manipulations, which have many varieties. It depends on the type of procedure that will be relevant for a particular patient. According to this criterion, interventions for the correction of hallux valgus are divided into:
- On soft tissues. In this case, the treatment of hallux valgus in children and adults in the early stages of the development of pathology can be the use of the Silver and McBride technique. They are relevant only for stage I of the disease.
- A combination of effects on bone and soft tissue structures to treat foot deformities, for example the Schede operation.
- On the bones. This type of surgery is called an osteotomy, which has many varieties. It is often used for moderate to severe foot deformities in adults.
Modern methods of surgical treatment of patients with foot deformities allow, in many cases, to perform the intervention percutaneously or using a laser, for example, resurfacing the "bone" for hallux abductus valgus. If it is possible to carry out a minimally invasive therapy for hallux valgus deformities, the advantages are evident:
- rapid rehabilitation times;
- absence of large incisions and seams;
- eliminating the need for long-term hospitalization;
- low risk of complications.
The goal of any type of surgery is to bring the foot closer to its natural, normal state. However, the doctor takes into account the individual structure of the patient's legs, since it is unique.
Recovery after surgery to correct hallux valgus requires variable times: from 2 weeks to 4 months, depending on the extent of the surgery and its complexity. During the recovery period, you will need to wear special shoes, follow the doctor's recommendations and use medications.
Features of treatment in children
Parents are often the first to notice bunions in children. If it appears early, it becomes evident around the age of one year, when the child begins to walk. Sometimes a pediatrician notices a deviation and can show it and refer you for a consultation with an orthopedist.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the situation can be corrected using conservative therapeutic methods. If the child's arch is in the valgus position, in most cases the problem can be solved without surgery.
If at an early age, when placing the feet, a valgus curvature is formed, massage, physiotherapy and physical therapy are used. However, one of the main ways to correct the situation is to wear orthopedic shoes. It is selected individually; as the child grows and the angle of the foot changes, it must be replaced.
Surgical treatment is used very rarely, and the question of its choice is always approached individually. With a small degree of damage, they try not to use radical treatment.
The prognosis for the treatment of first toe deformities and valgus in general in children is often positive. If you follow all the doctor's recommendations and systematic observation, you can completely restore the normal appearance and functionality of the foot.
Which doctor is treating you?
Treatment of hallux valgus is traditionally carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist. It is this specialist who will help the patient if the first symptom of the disease is noticed or for preventive purposes. In case of childhood illness, the specialist must have the skills and experience in managing such patients. If radical treatment of hallux valgus is necessary, the participation of a surgeon will be necessary.
Forecast
With adequate and timely therapy, hallux valgus deformity can be successfully eliminated. In most cases it is possible to stop the pain and obtain the desired aesthetic cosmetic effect. The therapy is especially successful in young children, as well as in the initial stage of the development of the problem.
However, this is feasible if you follow all the recommendations of the specialist, as well as in case of early diagnosis. In severe situations, treatment of hallux valgus is also possible, but it will take more time and involve the use of more serious methods of intervention. There is a risk that in particularly advanced cases it may not be possible to completely restore the original conditions of the foot.
Prevention
There are no reliable methods to definitively prevent hallux valgus. It is multifactorial in nature and is often due to genetic predisposition. However, there are several ways to reduce the risk of it occurring or eliminate it at an early stage of development:
- regular preventive examination by an orthopedist-traumatologist;
- timely detection and treatment of flat feet;
- wear comfortable shoes, excluding stilettos for women;
- if necessary, use of orthopedic insoles;
- weight control, keeping it in a normal and optimal state;
- compliance with the norms of rest and work, especially if a person's professional activity is associated with increased stress on the legs;
- correct and balanced nutrition, abandoning bad habits;
- a moderate level of physical activity, which implies the absence of both physical inactivity and excessive stress on the legs.
In a modern medical center you can undergo modern diagnostics and treatment of hallux valgus at any stage of its development.